A single-file real-time speech-to-text tool that runs entirely on your own computer—like your personal stenographer: it writes down whatever you say.

Features at a Glance (Quick Overview)
- 🎤 Real-Time Transcription: Extremely low latency (within ~3 seconds), see text appear as you speak.
- 📝 Smart Punctuation: Automatically adds commas, periods, question marks, etc., to paused sentences, outputting fluent paragraphs.
- 🔐 Purely Local Operation: All audio and text are processed on your machine, not uploaded to the internet (requires manual model download on first run).
- 📂 Automatic Audio Recording: The program saves
.wavaudio files for easy review. - 📋 Export & Copy: Copy to clipboard or export as
.txtwith one click.
Preparation Before Use (Three Steps, Beginner-Friendly)
Step 1: Install uv
If you haven't installed uv yet, please refer to the instructions in my previous article for installation (details omitted here).
The full single-file code
app.pyis included later in this article, and a download link forapp.pyis also provided.
Step 2: Download the Program and Model Files
Program Code: Copy the complete code at the end of this article into a new text document and save it as
app.py.Note: In your file explorer, enable "View" → check "Show file extensions" to ensure the file is indeed named
app.pyand notapp.py.txt.Model: This is the "brain" for recognition accuracy. Please download the model archive (click manually or copy to your browser):
https://github.com/jianchang512/stt/releases/download/0.0/realtimestt-models.7zAfter downloading, extract it and place the following 4 files into the
onnxfolder created in the next step:ctc.model.onnxdecoder.onnxencoder.onnxtokens.txt
Tip: If you forget to download the model, the program will prompt you with a pop-up window on first run and automatically copy the download URL to your clipboard for easy pasting into your browser.
Step 3: Organize the Folder Structure
Create a new folder on your computer, e.g., SpeechToTextTool, and place files as required below:
SpeechToTextTool/
|- app.py
|- onnx/
|- ctc.model.onnx
|- decoder.onnx
|- encoder.onnx
|- tokens.txt- Place
app.pyin the root directory (not insideonnx). - The
onnxfolder must exist and contain the 4 model-related files listed above. - The program will automatically generate an
outputfolder in the root directory to store audio recordings and text backups.
Launching the Program (Step-by-Step, Very Simple)
- Open the folder where you placed
app.py. - In the File Explorer address bar, clear it and type
cmd, then press Enter — this opens a command window at that folder location. - In the command line, enter:
uv run app.pyuv will create a runtime environment and install dependencies (the first run will be slower, please be patient). Upon successful launch, the program interface will pop up (see image below):
Interface and Operation Instructions
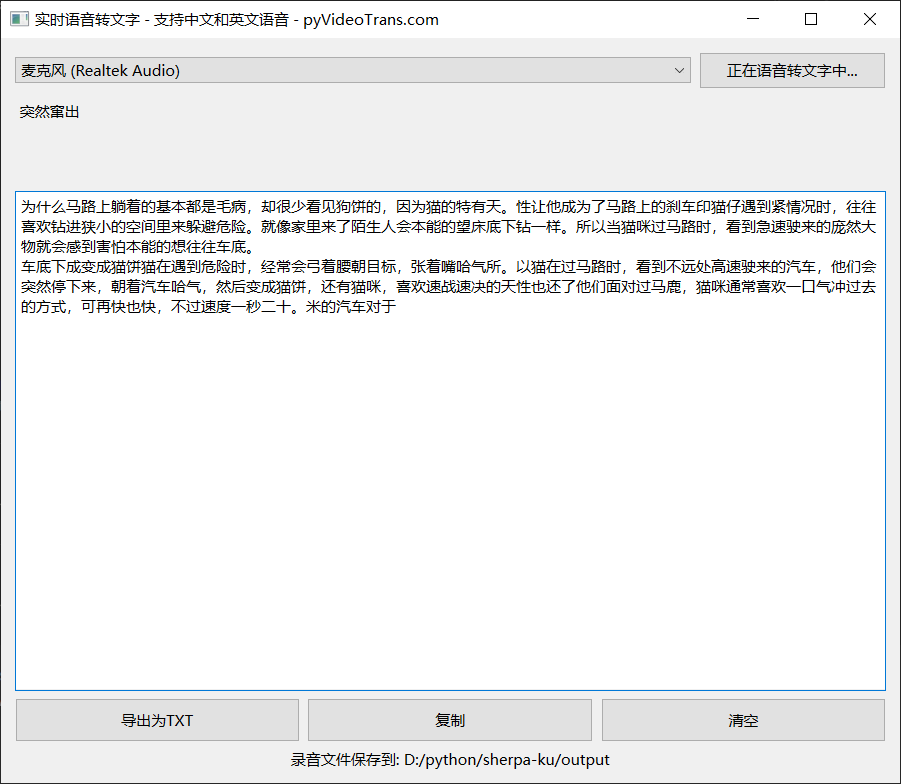
Key Interface Points:
Select Microphone: The program automatically lists microphone devices detected by your system; generally, selecting "Default" is fine.
Start/Stop Button: Click "Start Real-Time Speech-to-Text" to begin transcription; click again to stop.
Real-Time Display Area: Shows "temporary text being recognized" as you speak.
Final Result Area: When the system detects a pause (about 2–3 seconds), it adds punctuation to the current sentence and places it here as a "completed" paragraph.
Function Button Area:
- Export as TXT: Saves the final result as a
.txtfile. - Copy: Copies all recognition results to the clipboard with one click.
- Clear: Clears the result area.
- Export as TXT: Saves the final result as a
Recording File Location Display: The program creates an
outputfolder in the running directory to save.wavand.txtbackups. Click the path to open the folder and view files.
Runtime Details and Precautions (Avoid Pitfalls)
- Sample Rate & Device: The program reads the microphone at a 48 kHz sample rate (internal conversion is performed as needed). If your microphone is occupied by another program, it may fail to start; close the application using the microphone first.
- Models Must Be in Place: If the
onnxdirectory lacks model files, the program will display a pop-up and automatically copy the download link to your clipboard. - First Run is Slow:
uvinstalls dependencies on the first run; the time depends on your network and computer, just be patient. - Privacy: All audio and text are saved on your machine and are not uploaded to the internet.
- Accent, Noise: Recognition works best with standard Mandarin pronunciation and a quiet environment; heavy noise or dialects will reduce accuracy.
- Recording Save Location: The
*.wavfiles and automatically backed-up*.txtfiles in theoutputfolder can be used for review or secondary processing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How accurate is the recognition? A: Very good for standard Mandarin, clear pronunciation, and low-noise environments. Accuracy decreases with strong accents or significant background noise.
Q: What languages are supported? A: Currently optimized for Chinese Mandarin; it can also recognize common English words or phrases, but the focus is primarily on Chinese.
Q: What if clicking Start does nothing? A: First, confirm the model files are in the
onnxfolder (see Step 3); confirm the microphone is connected and the system has granted the app permission to use it; check ifuv runis executed from the correct folder.Q: Is the program free? A: Completely free.
Tips (For Smoother Use)
- Meeting Scenario: Place your laptop or microphone close to the speaker to ensure good audio capture quality.
- Backup: After each meeting or important recording, save a copy of the
.wavand.txtfiles from theoutputfolder to cloud storage or an external drive. - Automation: If you're familiar with scripting, you can create a batch file or shortcut to run
uv run app.pydirectly by double-clicking in the program folder. - Save this code as
start.batto enable quick launch by double-clickingstart.bat:
@echo off
call uv run app.py
pauseComplete Program Code (Copy and Save as app.py)
If copying from WeChat is inconvenient, you can also open this link in your browser to download:
https://github.com/jianchang512/stt/releases/download/0.0/app.py
# /// script
# requires-python = "==3.12.*"
# dependencies = [
# "librosa>=0.11.0",
# "numpy>=2.3.4",
# "onnxruntime>=1.23.2",
# "pyside6>=6.10.0",
# "sherpa-onnx>=1.12.15",
# "sounddevice>=0.5.3",
# "soundfile>=0.13.1",
# ]
#
# [[tool.uv.index]]
# url = "https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/pypi/web/simple"
#
# ///
import sys,os
import time
import threading
from pathlib import Path
import sherpa_onnx
import onnxruntime
import numpy as np
import sounddevice as sd
import wave
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QComboBox, QPushButton, QPlainTextEdit, QFileDialog,QLabel
from PySide6.QtCore import QThread, Signal,Qt,QUrl
from PySide6.QtGui import QIcon, QCloseEvent,QDesktopServices
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QMessageBox
ROOT_DIR=Path(os.getcwd()).as_posix()
MODEL_DIR=f'{ROOT_DIR}/onnx'
OUT_DIR=f'{ROOT_DIR}/output'
Path(MODEL_DIR).mkdir(exist_ok=True)
Path(OUT_DIR).mkdir(exist_ok=True)
CTC_MODEL_FILE=f"{MODEL_DIR}/ctc.model.onnx"
PAR_ENCODER = f"{MODEL_DIR}/encoder.onnx"
PAR_DECODER = f"{MODEL_DIR}/decoder.onnx"
PAR_TOKENS = f"{MODEL_DIR}/tokens.txt"
class OnnxModel:
def __init__(self):
session_opts = onnxruntime.SessionOptions()
session_opts.log_severity_level = 3 # error level
self.sess = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(CTC_MODEL_FILE, session_opts)
self._init_punct()
self._init_tokens()
def _init_punct(self):
meta = self.sess.get_modelmeta().custom_metadata_map
punct = meta["punctuations"].split("|")
self.id2punct = punct
self.punct2id = {p: i for i, p in enumerate(punct)}
self.dot = self.punct2id["。"]
self.comma = self.punct2id[","]
self.pause = self.punct2id["、"]
self.quest = self.punct2id["?"]
self.underscore = self.punct2id["_"]
def _init_tokens(self):
meta = self.sess.get_modelmeta().custom_metadata_map
tokens = meta["tokens"].split("|")
self.id2token = tokens
self.token2id = {t: i for i, t in enumerate(tokens)}
unk = meta["unk_symbol"]
assert unk in self.token2id, unk
self.unk_id = self.token2id[unk]
def __call__(self, text: str) -> str:
word_list = text.split()
words = []
for w in word_list:
s = ""
for c in w:
if len(c.encode()) > 1:
if s == "":
s = c
elif len(s[-1].encode()) > 1:
s += c
else:
words.append(s)
s = c
else:
if s == "":
s = c
elif len(s[-1].encode()) > 1:
words.append(s)
s = c
else:
s += c
if s:
words.append(s)
ids = []
for w in words:
if len(w[0].encode()) > 1:
# a Chinese phrase:
for c in w:
ids.append(self.token2id.get(c, self.unk_id))
else:
ids.append(self.token2id.get(w, self.unk_id))
segment_size = 30
num_segments = (len(ids) + segment_size - 1) // segment_size
punctuations = []
max_len = 200
last = -1
for i in range(num_segments):
this_start = i * segment_size
this_end = min(this_start + segment_size, len(ids))
if last != -1:
this_start = last
inputs = ids[this_start:this_end]
out = self.sess.run(
[
self.sess.get_outputs()[0].name,
],
{
self.sess.get_inputs()[0]
.name: np.array(inputs, dtype=np.int32)
.reshape(1, -1),
self.sess.get_inputs()[1].name: np.array(
[len(inputs)], dtype=np.int32
),
},
)[0]
out = out[0] # remove the batch dim
out = out.argmax(axis=-1).tolist()
dot_index = -1
comma_index = -1
for k in range(len(out) - 1, 1, -1):
if out[k] in (self.dot, self.quest):
dot_index = k
break
if comma_index == -1 and out[k] == self.comma:
comma_index = k
if dot_index == -1 and len(inputs) >= max_len and comma_index != -1:
dot_index = comma_index
out[dot_index] = self.dot
if dot_index == -1:
if last == -1:
last = this_start
if i == num_segments - 1:
dot_index = len(inputs) - 1
else:
last = this_start + dot_index + 1
if dot_index != -1:
punctuations += out[: dot_index + 1]
ans = []
for i, p in enumerate(punctuations):
t = self.id2token[ids[i]]
if ans and len(ans[-1][0].encode()) == 1 and len(t[0].encode()) == 1:
ans.append(" ")
ans.append(t)
if p != self.underscore:
ans.append(self.id2punct[p])
return "".join(ans)
# Create recognizer
def create_recognizer():
encoder = PAR_ENCODER
decoder = PAR_DECODER
tokens = PAR_TOKENS
recognizer = sherpa_onnx.OnlineRecognizer.from_paraformer(
tokens=tokens,
encoder=encoder,
decoder=decoder,
num_threads=2,
sample_rate=16000,
feature_dim=80,
enable_endpoint_detection=True,
rule1_min_trailing_silence=2.4,
rule2_min_trailing_silence=1.2,
rule3_min_utterance_length=20, # it essentially disables this rule
)
return recognizer
# Worker thread for transcription
class Worker(QThread):
new_word = Signal(str)
new_segment = Signal(str)
ready = Signal()
def __init__(self, device_idx, parent=None):
super().__init__(parent)
self.device_idx = device_idx
self.running = False
self.sample_rate = 48000
self.samples_per_read = int(0.1 * self.sample_rate)
def run(self):
devices = sd.query_devices()
if len(devices) == 0:
return
print(f'Using microphone: {devices[self.device_idx]["name"]}')
PUNCT_MODEL = OnnxModel()
recognizer = create_recognizer()
stream = recognizer.create_stream()
mic_stream = sd.InputStream(
device=self.device_idx,
channels=1,
dtype="float32",
samplerate=self.sample_rate
)
mic_stream.start()
timestamp = time.strftime("%Y%m%d_%H-%M-%S")
txt_file = open(f"{OUT_DIR}/{timestamp}.txt", 'a')
wav_file = wave.open(f"{OUT_DIR}/{timestamp}.wav", 'wb')
wav_file.setnchannels(1)
wav_file.setsampwidth(2) # int16
wav_file.setframerate(self.sample_rate)
self.ready.emit() # Emit ready signal after initialization
self.running = True
last_result = ""
while self.running:
samples, _ = mic_stream.read(self.samples_per_read)
samples_int16 = (samples * 32767).astype(np.int16)
wav_file.writeframes(samples_int16.tobytes())
samples = samples.reshape(-1)
stream.accept_waveform(self.sample_rate, samples)
while recognizer.is_ready(stream):
recognizer.decode_stream(stream)
is_endpoint = recognizer.is_endpoint(stream)
result = recognizer.get_result(stream)
if result != last_result:
self.new_word.emit(result)
last_result = result
if is_endpoint:
if result:
punctuated = PUNCT_MODEL(result)
txt_file.write(punctuated)
self.new_segment.emit(punctuated)
recognizer.reset(stream)
mic_stream.stop()
wav_file.close()
txt_file.close()
# Main GUI window
class RealTimeWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle('Real-Time Speech-to-Text - Supports Chinese and English - pyVideoTrans.com')
self.layout = QVBoxLayout(self)
# Microphone selection
self.mic_layout = QHBoxLayout()
self.combo = QComboBox()
self.populate_mics()
self.mic_layout.addWidget(self.combo)
self.start_button = QPushButton('Start Real-Time Speech-to-Text')
self.start_button.setCursor(Qt.PointingHandCursor)
self.start_button.setMinimumHeight(30)
self.start_button.setMinimumWidth(150)
self.start_button.clicked.connect(self.toggle_transcription)
self.mic_layout.addWidget(self.start_button)
self.layout.addLayout(self.mic_layout)
# Real-time text
self.realtime_text = QPlainTextEdit()
self.realtime_text.setReadOnly(True)
self.realtime_text.setStyleSheet("background: transparent; border: none;")
self.realtime_text.setMaximumHeight(80)
self.layout.addWidget(self.realtime_text)
# Text edit for segments
self.textedit = QPlainTextEdit()
self.textedit.setReadOnly(True)
self.textedit.setMinimumHeight(400)
self.layout.addWidget(self.textedit)
# Buttons layout
self.button_layout = QHBoxLayout()
self.export_button = QPushButton('Export as TXT')
self.export_button.clicked.connect(self.export_txt)
self.export_button.setCursor(Qt.PointingHandCursor)
self.export_button.setMinimumHeight(35)
self.button_layout.addWidget(self.export_button)
self.copy_button = QPushButton('Copy')
self.copy_button.setMinimumHeight(35)
self.copy_button.setCursor(Qt.PointingHandCursor)
self.copy_button.clicked.connect(self.copy_textedit)
self.button_layout.addWidget(self.copy_button)
self.clear_button = QPushButton('Clear')
self.clear_button.setMinimumHeight(35)
self.clear_button.setCursor(Qt.PointingHandCursor)
self.clear_button.clicked.connect(self.clear_textedit)
self.button_layout.addWidget(self.clear_button)
self.layout.addLayout(self.button_layout)
self.btn_opendir=QPushButton(f"Recording files saved to: {OUT_DIR}")
self.btn_opendir.setStyleSheet("background-color:transparent;border:0;")
self.btn_opendir.clicked.connect(self.open_dir)
self.layout.addWidget(self.btn_opendir)
self.worker = None
self.transcribing = False
def check_model_exist(self):
if not Path(PAR_ENCODER).exists() or not Path(CTC_MODEL_FILE).exists() or not Path(PAR_DECODER).exists():
reply = QMessageBox.information(self,'Missing models required for real-time speech-to-text, please download',
f'The model download URL has been copied to your clipboard. Please paste it into your browser address bar to download.\n\nTo keep the software package size small, models are not included by default. After downloading and extracting, place the 4 files inside into the {MODEL_DIR} folder.'
)
QApplication.clipboard().setText('https://github.com/jianchang512/stt/releases/download/0.0/realtimestt-models.7z')
return False
return True
def open_dir(self):
QDesktopServices.openUrl(QUrl.fromLocalFile(OUT_DIR))
def populate_mics(self):
devices = sd.query_devices()
input_devices = [d for d in devices if d['max_input_channels'] > 0]
if not input_devices:
print("No available microphones found")
sys.exit(0)
default_idx = sd.default.device[0]
default_item = 0
for i, d in enumerate(input_devices):
self.combo.addItem(d['name'], d['index'])
if d['index'] == default_idx:
default_item = i
self.combo.setCurrentIndex(default_item)
def toggle_transcription(self):
if self.check_model_exist() is not True:
return
if not self.transcribing:
self.realtime_text.setPlainText('Please wait...')
device_idx = self.combo.currentData()
self.worker = Worker(device_idx)
self.worker.new_word.connect(self.update_realtime)
self.worker.new_segment.connect(self.append_segment)
self.worker.ready.connect(self.update_realtime_ready)
self.worker.start()
self.start_button.setText('Speech-to-Text in progress...')
self.transcribing = True
else:
if self.worker:
self.worker.running = False
self.worker.wait()
self.worker = None
self.start_button.setText('Start Real-Time Transcription')
self.transcribing = False
remaining_text = self.realtime_text.toPlainText().strip()
if remaining_text:
self.textedit.appendPlainText(remaining_text)
scrollbar = self.textedit.verticalScrollBar()
scrollbar.setValue(scrollbar.maximum())
self.realtime_text.clear()
def update_realtime(self, text):
self.realtime_text.setPlainText(text)
scrollbar = self.realtime_text.verticalScrollBar()
scrollbar.setValue(scrollbar.maximum())
def update_realtime_ready(self):
self.realtime_text.setPlainText('Please speak...')
def append_segment(self, text):
self.textedit.appendPlainText(text)
scrollbar = self.textedit.verticalScrollBar()
scrollbar.setValue(scrollbar.maximum())
def export_txt(self):
text=self.textedit.toPlainText().strip()
if not text:
return
file_name, _ = QFileDialog.getSaveFileName(self, "Save TXT", "", "Text files (*.txt)")
if file_name:
if not file_name.endswith(".txt"):
file_name += ".txt"
with open(file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(text)
def copy_textedit(self):
text = self.textedit.toPlainText()
QApplication.clipboard().setText(text)
def clear_textedit(self):
self.textedit.clear()
def closeEvent(self, event: QCloseEvent):
if self.transcribing:
self.toggle_transcription()
super().closeEvent(event)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = RealTimeWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())You Can Start Right Away
Follow the three preparation steps above, run uv run app.py to launch. If you encounter issues, first check if the onnx files are complete, if the microphone is recognized by the system, and if uv is successfully installed.
