Baidu Translation API
1. Apply for the Baidu Translation API
Open the Baidu Translation API console at https://fanyi-api.baidu.com/api/trans/product/desktop. If you are not logged in, you will be redirected to the registration/login page. Please log in and then reopen the link.
After opening the page, click on "Activate Other Translation Services".
If you haven't applied before, click on "General Text Translation", then click "Next" at the bottom.
On the next page, fill in the relevant information. Note: Do NOT fill in the "Server Address" field. If you do, the API will only be callable from that specific IP address. Once your IP changes or you switch computers, the interface will report an error. This is a common issue many users encounter with the Baidu Translation API—the account is fine, but it reports an "unauthorized" error.
After your application is approved, return to the management console and scroll to the bottom. You will see your APP ID and Secret Key.
Fill them in wherever needed.
2. Fill in the software settings: Go to the top-left menu -> Settings -> Baidu Translation Settings, and enter the corresponding APPID and Secret Key.
3. Free Quota
Starting August 1, 2022, the free call quota for the Baidu General Translation API Standard Edition has been adjusted to 50,000 characters/month, and the Advanced Edition to 1 million characters/month.
As you can see, Baidu's free quota is quite low and generally insufficient for regular use. For heavy usage, consider upgrading to a paid plan.
In comparison, Tencent Translation offers a much higher free quota of up to 5 million characters per month.
Important Notes:
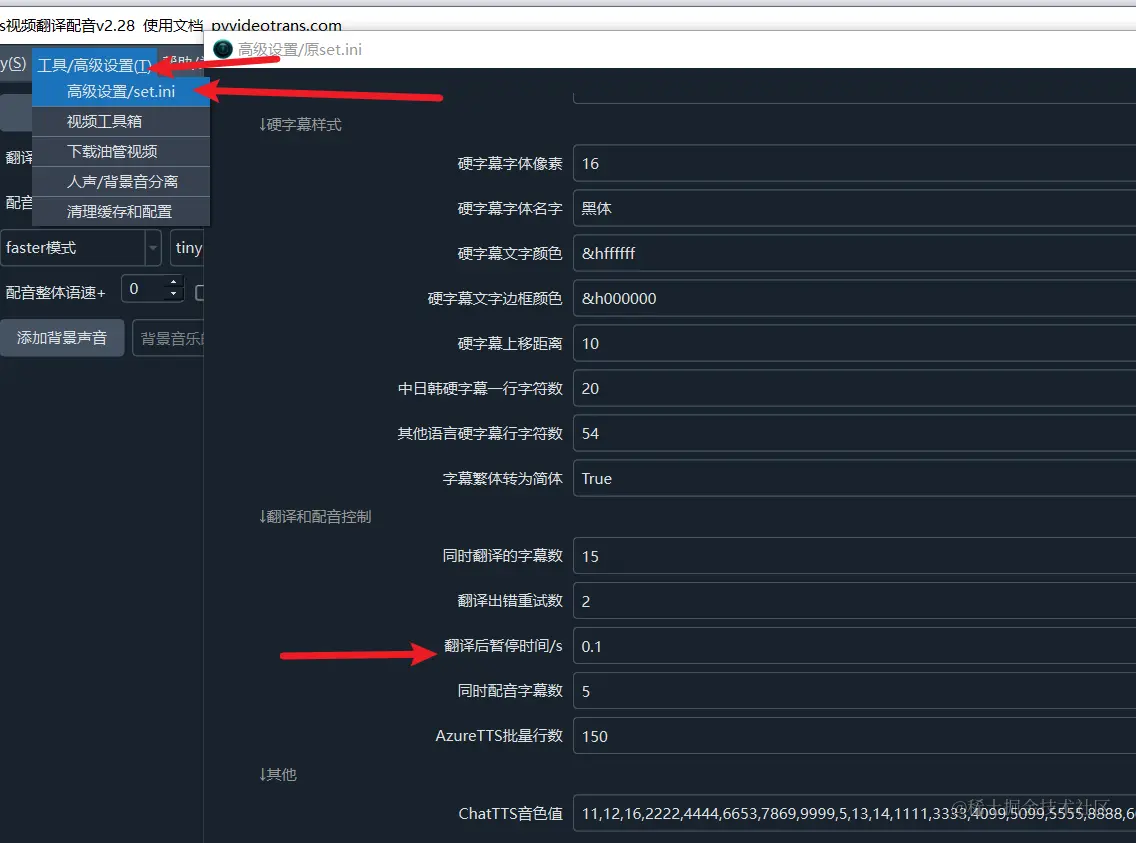
Most AI translation channels may limit the number of requests per minute. If you encounter an error indicating that the request frequency has been exceeded, you can adjust the settings in the software: Menu -> Tools/Advanced Settings -> Advanced Settings/set.ini -> Pause Time After Translation. Set a value in seconds, for example, 30, which means the software will wait 30 seconds after each translation before proceeding to the next one, avoiding frequency limit errors.